|

M-theory, the theory formerly known as Strings
The Standard Model
In the standard model of particle physics, particles are considered to be points
moving through space, tracing out a line called the World Line. To take into
account the different interactions observed in Nature one has to provide
particles with more degrees of freedom than only their position and velocity,
such as mass, electric charge, color (which is the "charge" associated
with the strong interaction) or spin.
The standard model was designed within a framework known as Quantum Field
Theory (QFT), which gives us the tools to build theories consistent both with
quantum mechanics and the special theory of relativity. With these tools,
theories were built which describe with great success three of the four known
interactions in Nature: Electromagnetism, and the Strong and Weak nuclear
forces. Furthermore, a very successful unification between Electromagnetism and
the Weak force was achieved (Electroweak Theory), and promising ideas put
forward to try to include the Strong force. But unfortunately the fourth
interaction, gravity, beautifully described by Einstein's General Relativity (GR),
does not seem to fit into this scheme. Whenever one tries to apply the rules of
QFT to GR one gets results which make no sense. For instance, the force between
two gravitons (the particles that mediate gravitational interactions), becomes
infinite and we do not know how to get rid of these infinities to get physically
sensible results.
String Theory
In String Theory, the myriad of particle types is replaced by a single
fundamental building block, a `string'. These strings can be closed, like loops,
or open, like a hair. As the string moves through time it traces out a tube or a
sheet, according to whether it is closed or open. Furthermore, the string is
free to vibrate, and different vibrational modes of the string represent the
different particle types, since different modes are seen as different masses or
spins.
One mode of vibration, or `note', makes the string appear as an electron,
another as a photon. There is even a mode describing the graviton, the particle
carrying the force of gravity, which is an important reason why String Theory
has received so much attention. The point is that we can make sense of the
interaction of two gravitons in String theory in a way we could not in QFT.
There are no infinities! And gravity is not something we put in by hand. It has
to be there in a theory of strings. So, the first great achievement of String
Theory was to give a consistent theory of quantum gravity, which resembles GR at
macroscopic distances. Moreover String Theory also possesses the necessary
degrees of freedom to describe the other interactions! At this point a great
hope was created that String Theory would be able to unify all the known forces
and particles together into a single `Theory of Everything'.
From Strings to Superstrings
The particles known in nature are classified according to their spin into bosons
(integer spin) or fermions (odd half integer spin). The former are the ones that
carry forces, for example, the photon, which carries electromagnetic force, the
gluon, which carries the strong nuclear force, and the graviton, which carries
gravitational force. The latter make up the matter we are made of, like the
electron or the quark. The original String Theory only described particles that
were bosons, hence Bosonic String Theory. It did not describe Fermions.
So quarks and electrons, for instance, were not included in Bosonic String
Theory.
By introducing Supersymmetry to Bosonic String Theory, we can obtain
a new theory that describes both the forces and the matter which make up the
Universe. This is the theory of superstrings. There are three different
superstring theories which make sense, i.e. display no mathematical
inconsistencies. In two of them the fundamental object is a closed string, while
in the third, open strings are the building blocks. Furthermore, mixing the best
features of the bosonic string and the superstring, we can create two other
consistent theories of strings, Heterotic String Theories.
However, this abundance of theories of strings was a puzzle: If we are
searching for the theory of everything, to have five of them is an embarrassment
of riches! Fortunately, M-theory came to save us.
Extra dimensions...
One of the most remarkable predictions of String Theory is that space-time has
ten dimensions! At first sight, this may be seen as a reason to dismiss the
theory altogether, as we obviously have only three dimensions of space and one
of time. However, if we assume that six of these dimensions are curled up very
tightly, then we may never be aware of their existence. Furthermore, having
these so-called compact dimensions is very beneficial if String Theory is to
describe a Theory of Everything. The idea is that degrees of freedom like the
electric charge of an electron will then arise simply as motion in the extra
compact directions! The principle that compact dimensions may lead to unifying
theories is not new, but dates from the 1920's, since the theory of Kaluza and
Klein. In a sense, String Theory is the ultimate Kaluza-Klein theory.
For simplicity, it is usually assumed that the extra dimensions are wrapped
up on six circles. For realistic results they are treated as being wrapped up on
mathematical elaborations known as Calabi-Yau Manifolds and Orbifolds.
Apart from the fact that instead of one there are five different, healthy
theories of strings (three superstrings and two heterotic strings) there was
another difficulty in studying these theories: we did not have tools to explore
the theory over all possible values of the parameters in the theory. Each theory
was like a large planet of which we only knew a small island somewhere on the
planet. But over the last four years, techniques were developed to explore the
theories more thoroughly, in other words, to travel around the seas in each of
those planets and find new islands. And only then it was realized that those
five string theories are actually islands on the same planet, not different
ones! Thus there is an underlying theory of which all string theories are only
different aspects. This was called M-theory. The M might stand for
Mother of all theories or Mystery, because the planet we call M-theory is still
largely unexplored.
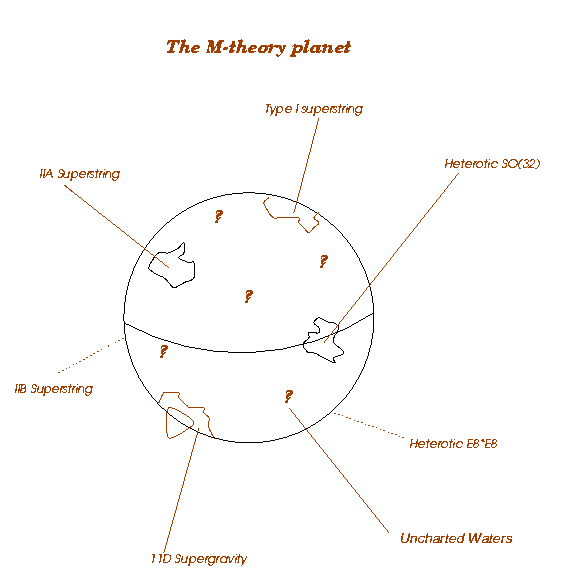
There is still a third possibility for the M in M-theory. One of the islands
that was found on the M-theory planet corresponds to a theory that lives not in
10 but in 11 dimensions. This seems to be telling us that M-theory should be
viewed as an 11 dimensional theory that looks 10 dimensional at some points in
its space of parameters. Such a theory could have as a fundamental object a
Membrane, as opposed to a string. Like a drinking straw seen at a distance, the
membranes would look like strings when we curl the 11th dimension into a small
circle.
Black Holes in M-theory
Black Holes have been studied for many years as configurations of spacetime in
General Relativity, corresponding to very strong gravitational fields. But since
we cannot build a consistent quantum theory from GR, several puzzles were raised
concerning the microscopic physics of black holes. One of the most intriguing
was related to the entropy of Black Holes. In thermodynamics, entropy is the
quantity that measures the number of states of a system that look the same. A
very untidy room has a large entropy, since one can move something on the floor
from one side of the room to the other and no one will notice because of the
mess - they are equivalent states. In a very tidy room, if you change anything
it will be noticeable, since everything has its own place. So we associate
entropy to disorder. Black Holes have a huge disorder. However, no one knew what
the states associated to the entropy of the black hole were. The last four years
brought great excitement in this area. Similar techniques to the ones used to
find the islands of M-theory, allowed us to explain exactly what states
correspond to the disorder of some black holes, and to explain using fundamental
theory the thermodynamic properties that had been deduced previously using less
direct arguments.
Many other problems are still open, but the application of string theory to
the study of Black Holes promises to be one of the most interesting topics for
the next few years.
[Back][Cosmology][Black
holes][Cosmic
strings][Inflation][Quantum
Gravity][Home][Next]
|
